NEW DELHI :
Badruddin Tyabji, the grandson of freedom fighter and third Congress President by the same name, was entrusted with arrangements for the inaugural Republic Day celebrations in 1950.
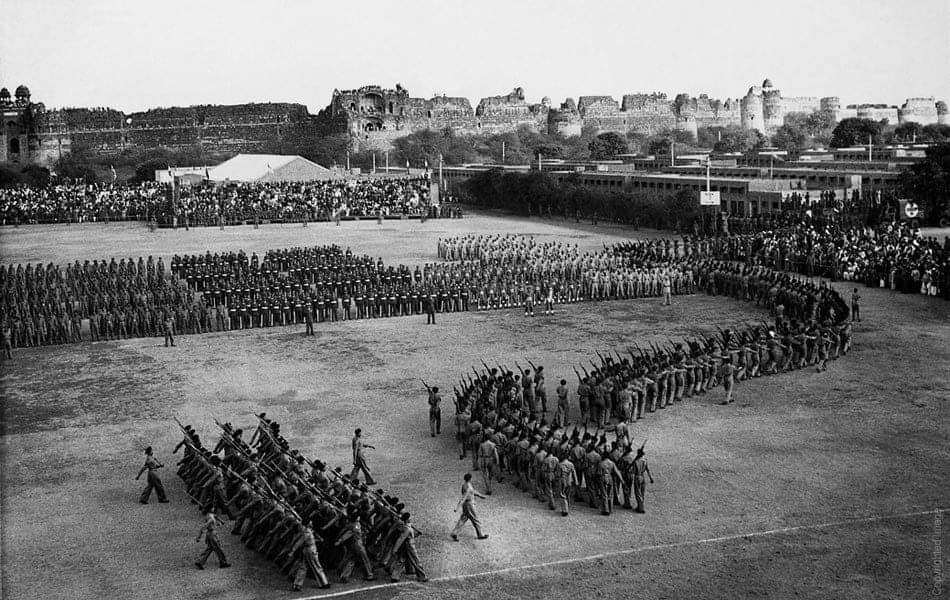

HISTORIC: National Stadium during the first Republic Day Parade. Old Fort is also visible
Every year on January 26, the Tyabji family sit together in their posh West End Colony house (near Vasant Vihar) to watch the Republic Day Parade which holds special significance for them.
Their late patriarch Badruddin Tyabji, a 1936 batch Punjab cadre Indian Civil Service officer, was responsible for looking after the arrangements of January 26, 1950 functions: first at the President House and later at Irwin Stadium (now Major Dhyan Chand National Stadium).
Tyabji’s painter wife Surayya Tyabji made the prototype of the Tri-colour on paper based on which the flag of cloth for Republic Day was made in Connaught Place.
“Just a couple of weeks before the first Republic Day, Prime Minister Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru entrusted me to look after the arrangements of the January 26 functions,” Tyabji told this writer in his south Delhi house in 1994.
He was also member secretary of the Constituent Assembly.
“I was called by Pt. Nehru and he gave me the huge responsibility for the historic day. I used to live at Sujan Singh Park during those days.”
From that day onwards, the tall and gracious Tyabji moved from the President House (now Rashtrapati Bhavan) to Irwin Stadium several times a day to finalise the arrangements as time was running out for the big day.
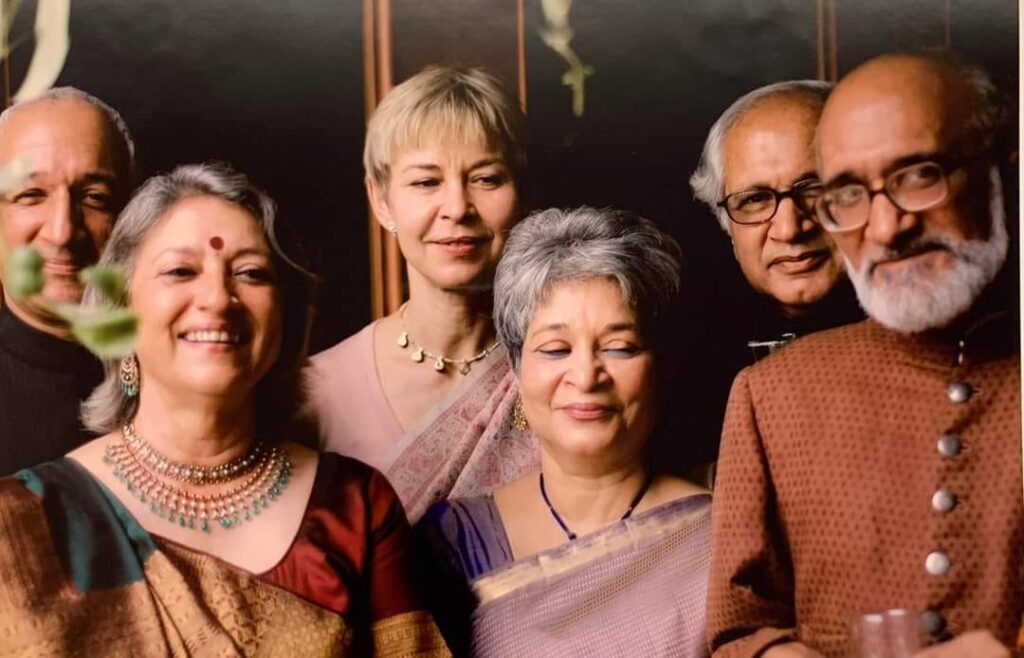

HAPPY FAMILY: The Tyabji clan including Laila Tyabji (centre, front row), who is a social worker, designer, writer and crafts activist
The big day for which Tyabji had worked so hard was also hectic for Rajendra Prasad, the soon-to-be first President of independent India. He marked the momentous occasion with a visit to Raj Ghat to pay homage to Gandhiji. He remained there for around 15 minutes.
But before the would-be President of India could get to the President House, C Rajagopalachari, the Governor General of India, had already reached there. The latter used to live in the double-storeyed bungalow at the then 10, Hastings Road, which was later renamed after him as Rajaji Marg. Edwin Lutyens, the chief architect of New Delhi, also lived in the bungalow, and so did Pranab Kumar Mukherjee, who also lived in that house after demitting his office of President of India.
“Dr Rajendra Prasad was sworn in as the country’s first President at around 9 am by the Governor General of India, C. Rajagopalachari. Rajvanshi Devi, his wife, and other family members were also there. The swearing-in ceremony was attended by over 500 guests, who had assembled inside the Durbar Hall. President Sukarno of Indonesia and several members of the Diplomatic Corps, members of the Constituent Assembly and prominent citizens had graced the occasion. The President was dressed in black achkan, white churidar and a white Gandhi cap. Pandit Nehru and his other Cabinet colleagues were sworn in soon after Rajendra Prasad,” recalled Tyabji, who was named after his grandfather, the third President of Indian National Congress.
Immediately after returning from Raj Ghat, Rajendra Prasad was sworn in. The Chief Justice of India, Sir Hiralal Kania, read the oath of office in Hindi. President Prasad repeated it sentence by sentence.
“The outgoing Governor General, C. Rajagopalachari; our first Prime Minister, Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru, beaming with pride and joy; the Deputy Prime Minister, Sardar Patel; cabinet ministers, judges of the Supreme Court and the Auditor-General of India, were present in the hall to witness the historic moment of India’s history. Pandit Nehru and his other cabinet colleagues were sworn in soon after.”
The national emblem of Ashoka Pillar with three lions was placed in the Durbar Hall for the first time near the throne where the British Viceroys used to sit.
A smiling statue of Lord Buddha was also placed behind the throne for the first time. Rajendra Prasad, the President, who greeted the large gathering smilingly with folded hands, made a short speech in Hindi and English, stating that it was a memorable day in our annals.
“Let us begin by offering our thanks to the Almighty Power who has enabled us to see this day; to the Father of the Nation who showed us and to the world at large his infallible method of Satyagraha, and led us on along it to freedom and to the numberless men and women, whose suffering and sacrifice have rendered the attainment of independence and establishment of this sovereign democratic Republic possible.”
The birth of the Republic was celebrated by the masses in the Capital through Prabhat Pheries (early morning movement of people singing patriotic songs). Outside the Durbar Hall, there were unforgettable scenes of jubilation. Large crowd of men, women and children had assembled in the forecourt of President House.
People raised slogans of Gandhiji-ki-jai and Vande Mataram.
After a dignified ceremony was held at the President House, the scene shifted to Irwin Stadium. The new President travelled to the stadium in a horse-drawn carriage and Delhi’s roads were lined up with enthusiastic crowd standing along the five-mile route with the Tri-colour in their hands. A huge crowd greeted the President’s entourage when it reached the vicinity of Connaught Place. And when the first President of India reached the stadium, he was welcomed with a booming 31-gun salute.
According to Tyabji, “Rajendra Prasad made a brief speech at the stadium. Later, students from various schools of the Capital presented cultural programmes.”
Old timers still recall that there were very few policemen guarding the VIPs inside the stadium. After the programme, the leaders mingled with the people. Nehru was mobbed by his admirers. He spent a good 20 minutes with them.
Tyabji, who could not sleep for several days ahead of the big occasion, was there managing the affairs carefully with his colleagues. Following very cold weather days in Delhi, brilliant sunshine greeted the Capital on January 26, 1950.
It was India’s defining moment, the day India truly freed itself from the shackles of colonialism to become a Republic. A truly sovereign state.
The talk of the first Republic Day cannot be complete without discussing the role of Tyabji’s wife, Surayya, in the making of the first Tri-colour.
According to Tyabji, “Once the Constituent Assembly finalised our Tri-colour with Ashok Dharma Chakra inside the flag, I was asked to furnish the model of Tri-colour on both paper and cloth.”
Without wasting any time, Badruddin Tyabji went straight to his Sujan Singh Park residence and asked his wife Surayya to make the Tri-colour on paper. She did not disappoint her husband. Once she made it on paper, Tyabji carried the design to the now defunct SC Tailors at Regal building of Connaught Place and asked them to make the Tri-colour in cloth. The rest, as they say, is history.
After retirement from government service, Tyabji also served as the Vice-Chancellor of Aligarh Muslim University in the 1960s.
He finally settled in Delhi and passed away in 1999. His wife, Suraiya, had died before him.
During one of our meetings, Tyabji had told me that when he came to Delhi from Hyderabad to appear for ICS examination, he was staying in Daryaganj.
He used to take a tonga to reach Metcalfe House in Civil Lines to appear for his examinations.
“Delhi was a very small city then. Except for old Delhi and villages, there was not much here. New Delhi was coming up,” he had said.
When India was divided on the basis of religion in 1947, he was perhaps one of the only two Muslim ICS officers who opted to stay in India instead of accepting Islamic Pakistan.
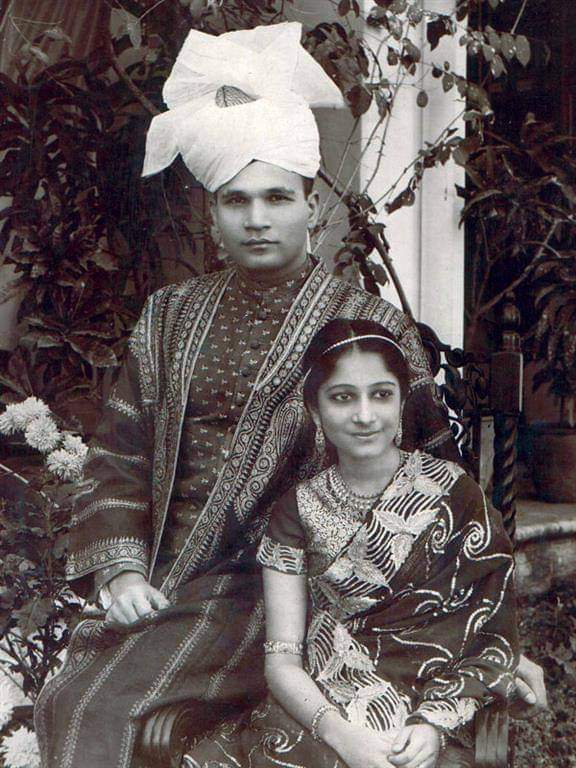
OFFICER RANK: Badruddin Tyabji was a 1936-batch ICS officer of Punjab cadre. His wife, Surayya was a painter
Tyabji’s first son, Hindal Ahmad, was an IAS officer. He passed away last year.
Tyabji’s daughter, Laila Tyabji is a noted social worker, designer, writer and crafts activist. She is one of the founders of Dastkar, a Delhi-based non-governmental organisation working for the revival of traditional crafts in India.
Like in the past, the Tyabji family would watch the annual parade this year too. After all, they are the true and proud first family of India’s Republic Day. Yet, they are so self-effacing.
source: http://www.thepatriot.in / The Patriot / Home> Cover Story / by Vivek Shukla / January 26th, 2024










