UTTAR PRADESH :
Synopsis
Former Indian Administrative Services officer Sabahat S Azim’s biggest challenge when he launched affordable healthcare chain Glocal Healthcare Systems was to prove that he could make the hospitals profitable.

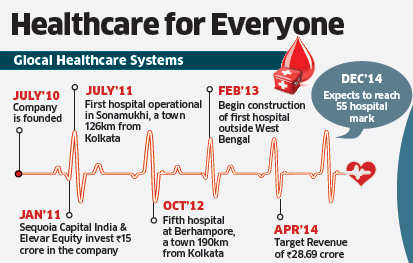
Within six months of launching the first Glocal hospital in July 2011 in Sonamukhi, a town 126km from Kolkata, the hospital had reached break-even. A model that the 37- yearold entrepreneur has now replicated in each of his other four hospitals. “They have proved that social good and profit can go hand in hand,” says Sandeep Farias, Founding Partner of Elevar Equity, which invested Rs 15 crore in the company along with Sequoia Capital India in January 2011. Most other hospitals that also offer affordable healthcare take up to two years to become profitable according to industry estimates.
Glocal is now expanding operations beyond West Bengal with plans to open 50 hospitals in Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand and Orissa by December 2014.
It was the untimely death of his father that led Azim, a trained medical doctor, to launch Glocal in July 2010. “My father died due to unnecessary treatments. I thought, if this can happen to me, a doctor and an IAS officer, what about others?” says Azim, who found an early supporter in M Damodaran, the former Chairman of Securities and Exchange Board of India (Sebi), who became the Chairman of the venture. Azim has known Damodaran since his time as Secretary to the Chief Minister of Tripura, a position he held between 2004 and 2006.
“He is my first sounding board for any idea. When I think of introducing something new, my first thought is ‘how will Mr Damodaran react?’” he says. At Glocal, his team has come up with a protocol-driven model, where the computerised system will help the doctor automate diagnosis of 42 diseases, ranging from ischaemic heart disease to malaria, which they identified as affecting 95% of the patients.
Other affordable ventures are also attempting to cater to the semi-urban and rural market. Like Glocal, eight-yearold Vaatsalya also sets up hospitals (smaller than 100 beds) in small cities and towns with a focus on primary and secondary care. However, Vaatsalya leases out pre-existing hospitals and other buildings and upgrades them to high-quality hospitals. Azim, a fan of Fountainhead—Ayn Rand’s paean to individualism, wanted to design a hospital with just essential infrastructure.
Timely backing from investors helped convert the idea into a business. “I had a 30-minute meeting with Sabahat and he spoke about focusing on a limited set of diseases that constitutes 95% of healthcare issues in the country. I was hooked by this powerful idea,” says Elevar’s Farias.
Sequoia’s Managing Director GV Ravishankar says Glocal fit their requirement of backing good entrepreneurs in large and attractive markets. Glocal charges patients around onefifth of the fees a hospital with similar infrastructure would otherwise charge. It charges Rs 10,000 for a caesarean section, which costs about Rs 50,000 in other private hospitals.
Azim points out that he is able to charge lower fees due to lower cost of infrastructure and by eliminating unnecessary procedures. While a typical 100-bed hospital is about 70,000 square feet in size, Glocal has been able to restrict it to 30,000 square feet thus keeping cost of construction lower. At around Rs 8 crore for a 100-bed hospital, a Glocal hospital is built at about 50% of the cost of a private secondary hospital. The company aims to reach over Rs 28 crore in revenue in fiscal year 2014. As Azim begins Glocal’s expansion beyond West Bengal, he is not resting on his laurels. “It has been exciting so far but there is much more work to do,” he says.
source: http://www.economictimes.indiatimes.com / The Economic Times / Home> Business News> Rise> Entrepreneurship / by Radhika P Nair, ET Bureau / January 25th, 2013








