PUNJAB / DELHI / Kolkata (WEST BENGAL) :
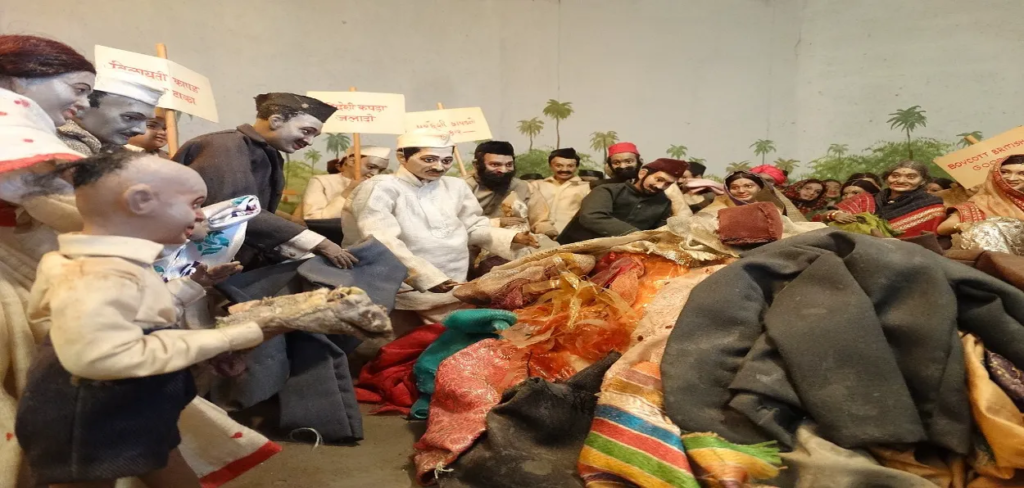

A diorama of Mahatma Gandhi leading satyagrahis in burning British clothes at Gandhi Smriti, New Delhi
Shaikh Mohammed Elias, son of Shaikh Mohammed Younus Fakhre Quaum often heard the story of his great-grandfather’s sacrifice for freedom.
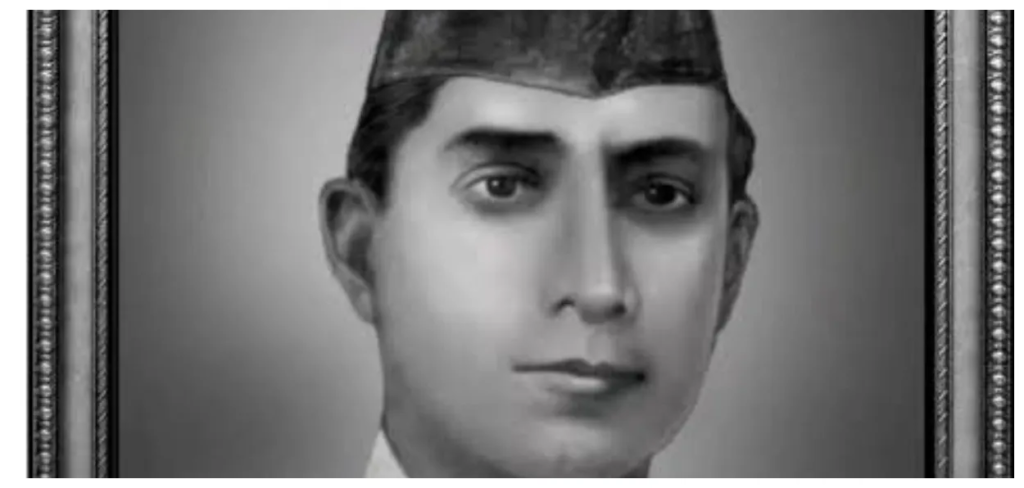
Fazal e Elahi Gorey Fakhre Quaum was a wealthy dealer of foreign goods in the 1940s when the British Empire had reached its zenith in glory and power.
In that pre-Independence era, all rich Indian merchants did well by shipping exorbitant British products from Britain and selling them in India. Because of his buoyant import-export business, Fazal e Elahi and his family lived in the lap of luxury. In those days, when no one had big branded cars, he was driving his grand Impala car around!
He and his family lived in Delhi. However, due to the exponential trade with Kolkata as the British capital, he moved there for business prospects. Since he was dealing with the British, he was given the moniker of Gorey Wale by the local people for a person who traded with the ‘whites’.
Rukhshi Kadiri Elias, entrepreneur and founder of Taajira-The Businesswoman, is the great grand-daughter-in-law of Fazal e Elahi. She told Awaz-The Voice that her great grand-father-in-law’s nickname Gorey Wale stuck on with him until an incident happened that elevated his name to a title awarded to him by the community, “Fakhre Quaum (Pride of the community).
Her father-in-law Shaikh Mohammed Younus Fakhre Quaum told her that even Mahatma Gandhi who fought vigilantly for the freedom of India would visit Kolkata and stay with him in his home during his visits. The family shares that Fazal e Elahi was a grand, gracious, and dignified man who lived by ethics.
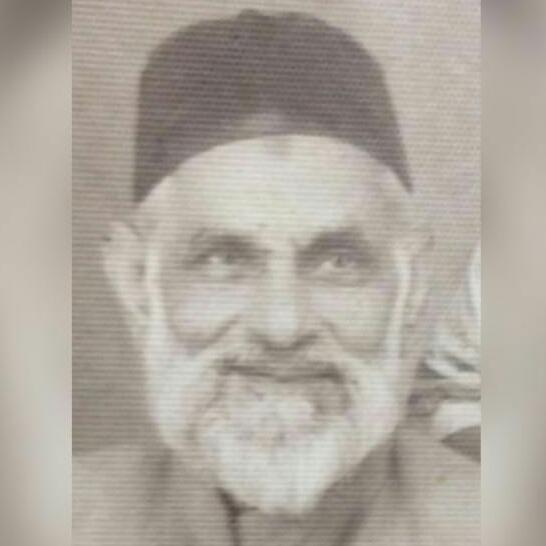

Fazal e Elahi Gorey Fakhre Quaum
The Swadeshi movement was gaining momentum with passions running high, and at this time, the boycott of British goods started to take on a fresh vigour. Ruskshi’s husband, Elias Mohammad Shaikh shares with the family how his great-grandfather, Fazal-e-Elahi in a defining moment took a bold step to join the Swadeshi movement.
Not thinking about himself, his family, or his future, he gathered the massive pile of British products from his warehouse, transported them to the Kolutolla crossing near the Mohammed Ali Library, and stacked them into a mountainous heap before the gaping crowds, he set the entire lot of goods ablaze in a roaring fire. His business days with the British were over and the Gorey Wale sealed all doors shut for any future trade with the British. Impressed, the crowds gave him the grand title of Fakhre Quaum, meaning “pride of the community.”
It only takes a spark to set a fire blazing. The locals watching him inspired by his sacrifice rushed back to their homes and gathered all the British products they were using, started to make little piles on that road and burn them up and soon the road was aflame with British merchandise. This was the start of the boycott movement in the Muslim community as well as all over Kolkata
Fazal-e-Elahi as a freedom fighter turned all his words into actions by bringing his entire warehouse of goods onto the streets to burn them. Setting an example to the others who never expected him to take this step, losing most of his business overnight, they perceived this act as going beyond mere words or loud speeches. It was a big turning point for himself as well as his family which would negatively impact his children bringing them financially down from this point forward.
He also used the remaining parts of his wealth to give make monetary contributions to the freedom struggle. To survive, he diversified into different Indian products and started making handmade candles, ink and other products and trading in the same. His son, Mohammad Younis also started on a small scale at a time when Bangladesh and West Bengal were one big state. During the Partition, while they had to shift from Bangladesh to Kolkata, they went through pain and struggle. Properties were confiscated and there was a great loss all around.
During the partition, many families of the freedom fighters split. Shaikh Mohammed Younus Fakhre Quaum had nine brothers and two sisters with most of the family living in Pakistan, while four remained in India.

Gandhi addressing Satyagrahis
Fazal-e-Elahi’s family was from Sargodha located in Punjab province of Pakistan. In the 1900s, looking for better prospects in trade, they traveled by caravan to the courts of the Mughal emperor of Delhi. The emperor encouraged people to come and settle down in the new city of Delhi. Learning about this, the family embarked on a journey to Delhi. During their travels on the way, the Hindu Punjabi traders met a seer by the name of Hazrat Shams Tabrez.
Highly influenced by his inspiring speeches and extraordinary demeanor, the entire party in the caravan converted to Islam. When they came and settled in Delhi, they became Delhi wallas known as Delhiwal meaning they were Punjabis settled in Delhi. They adopted Urdu, the court language of Delhi. Even today, while settled all over the world, they are known as Delhiwal and these groups of people are mostly concentrated in Kolkata and Delhi and all called Delhiwal.
While propagating the Quit India Movement, Fazal-e-Elahi rose quickly to become the president of the Baradari (brotherhood) of the Delhiwal community in Kolkata. When travelling down narrow lanes to build up the movement of Quit India, he abandoned driving his Impala car and started to use a horse.
Quoting her father-in-law, Rukshi says that India saw amazing unity during the Freedom Movement. Those days, one could make friends so easily, and it was the most normal thing to build bonding friendships with anyone across different communities. The freedom movement drew Indians into close ties where Indians forgot all their differences and only had the motive to defeat the Enemy.
Fazal-e-Elahi Gorey Fakhre Quaum sacrificed his flourishing business without thinking twice about it towards establishing the freedom of India setting patriotism waves over the community. Rukhshi says, “How many people will do that today is the question in this materialistically attached generation that we live in today. It was pure selflessness because Fazal-e-Elahi Gorey Fakhre Quaum considered India his own country. Such people will revive the spirit of India, sacrifice, and unity.” With a laugh she adds, “I could never think of throwing away my lovely tea set I bought in Britain, but he did it so easily.”
Rita Farhat Mukand is an independent writer and author
source: http://www.awazthevoice.in / Awaz, The Voice / Home> Story / by Rita Farhat Mukand / August 12th, 2024